Greenhouses need roofing that combines durability, light transmission, and energy efficiency. Many common coverings crack, fade, or let too much heat escape, affecting plant growth and maintenance costs. Polycarbonate panels for greenhouses provide a strong, UV-protected, and insulated solution.
This article explains the advantages of polycarbonate panels, how they support healthy plant growth, and key factors to consider when buying them for optimal greenhouse performance.

Polycarbonate Panels Overview
What Are Polycarbonate Panels
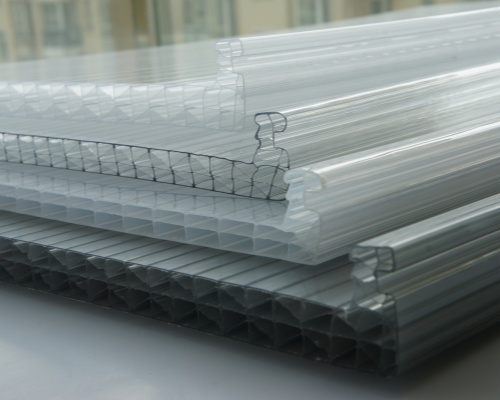
Polycarbonate panels are sheets made from a tough, transparent plastic. Manufacturers design these panels to be lightweight and strong. Gardeners often choose polycarbonate for greenhouse walls and roofs because it resists impact and weather.
Polycarbonate stands out for its ability to block harmful UV rays. This material also allows plenty of sunlight to pass through, which helps plants grow. Many people prefer polycarbonate over glass because it does not shatter easily.
| Feature | Polycarbonate Panels |
|---|---|
| Weight | Light |
| Strength | High |
| UV Protection | Yes |
| Light Transmission | Excellent |
How They Work in Greenhouses
Polycarbonate panels help create a stable environment inside greenhouses. These panels trap heat, which keeps plants warm during cold nights. The multiwall design of some polycarbonate panels adds extra insulation.
Gardeners use polycarbonate panels to diffuse sunlight. This reduces harsh shadows and spreads light evenly across all plants. The panels also protect plants from wind, rain, and hail.
Polycarbonate greenhouse panels require little maintenance. They resist cracking and do not need frequent cleaning. Many greenhouse owners find polycarbonate panels last for years, even in tough climates.
Benefits of Polycarbonate Panels
UV Protection and Light Transmission
Polycarbonate blocks harmful UV rays from reaching plants. This feature protects delicate leaves and flowers from sun damage. The material allows high light transmission, which helps plants grow strong and healthy.
Gardeners notice that polycarbonate diffuses light evenly throughout the greenhouse. Even on bright days, plants receive gentle light without harsh shadows. This balanced light environment supports a longer growing season.
Insulation and Heat Retention
Polycarbonate offers excellent insulation for greenhouses. The multiwall design traps air between layers, which improves thermal insulation. This helps maintain a stable temperature inside the greenhouse.
Strong insulation keeps plants warm during cold nights. Gardeners in cooler climates appreciate the energy savings and reduced heating costs. Polycarbonate supports healthy plant growth by preventing rapid temperature changes.
| Feature | Polycarbonate | Glass | PVC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulation | High | Low | Low |
| Heat Retention | Excellent | Poor | Poor |
| Energy Efficiency | Yes | No | No |
Durability and Safety
Polycarbonate is shatter-resistant and withstands impacts from hail or debris. The panels do not break easily, which makes them safer than glass. Gardeners choose polycarbonate for its long lifespan and low maintenance needs.
The material resists cracking and fading, even in harsh weather. Polycarbonate remains strong and clear for many years. Gardeners in windy or storm-prone areas rely on polycarbonate for reliable protection.
Drawbacks to Consider
Cost Factors
Polycarbonate panels often cost more than other greenhouse materials. The initial investment can surprise new gardeners. Many find that the price per square foot is higher than glass or PVC.
A simple table shows the typical price range:
| Material | Approximate Cost per Sq. Ft. |
|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | $2 – $4 |
| Glass | $1.50 – $3 |
| PVC | $1 – $2 |
Some gardeners choose polycarbonate for its long-term value. The panels last many years and need fewer replacements. Over time, the higher upfront cost may balance out with lower maintenance expenses.
Appearance and Aging
Polycarbonate panels look different from traditional glass. The panels often have a ribbed or frosted appearance. Some gardeners prefer the classic look of clear glass. Over time, polycarbonate can yellow or become cloudy. Sun exposure and weather cause this change. The panels may lose some clarity after several years.
Regular cleaning helps maintain the panels’ appearance. Some products offer UV coatings to slow yellowing. Still, no material stays perfect forever.
Polycarbonate Greenhouse Types
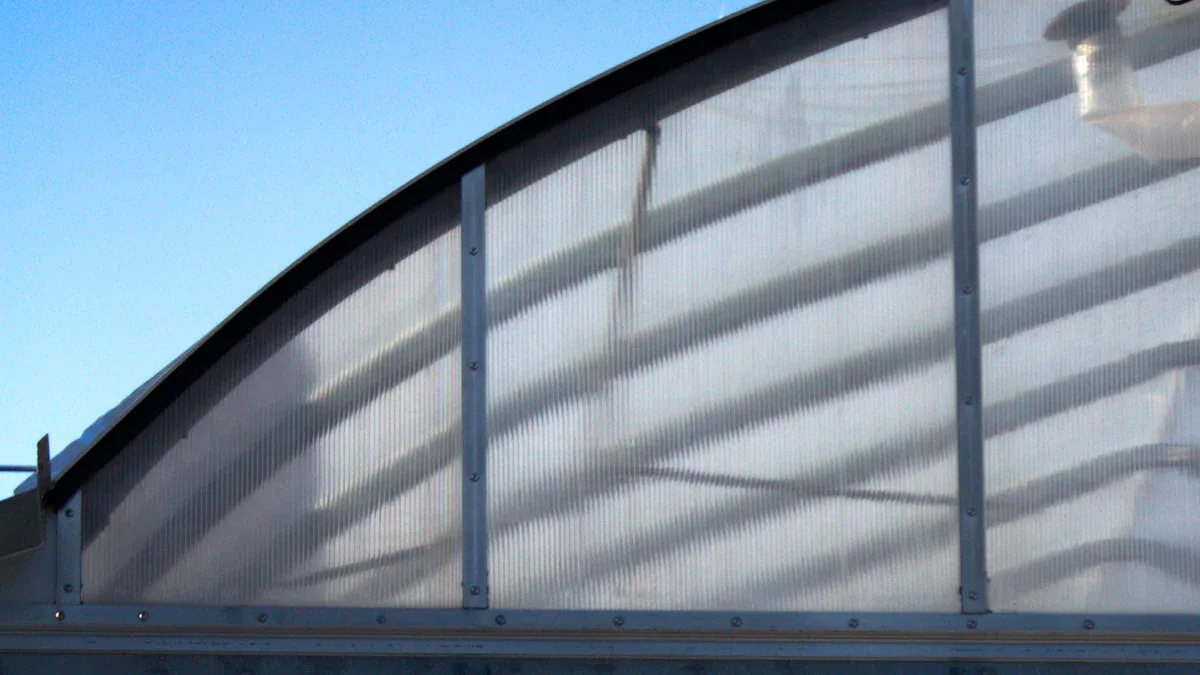

Single vs. Multiwall Panels
Gardeners often choose between single and multiwall polycarbonate for greenhouse construction. Single-layer panels allow maximum light to enter the greenhouse. Multiwall polycarbonate uses two or more layers separated by air pockets.
Multiwall panels provide better insulation than single-layer options. The air pockets help trap heat, which keeps plants warmer during cold weather. Multiwall polycarbonate also diffuses sunlight more evenly, reducing the risk of plant burn.
| Type | Insulation | Light Transmission | Weight | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-wall | Low | High | Light | Lower |
| Multiwall | High | Moderate | Heavier | Higher |
Choosing Thickness
The thickness of polycarbonate affects insulation, strength, and light transmission. Common thicknesses range from 4mm to 16mm. Thicker polycarbonate provides better insulation and withstands strong winds.
Thin panels allow more light but offer less protection against temperature changes. Thicker polycarbonate keeps the greenhouse warmer and reduces energy costs. Gardeners should match the thickness to their climate and growing needs.
A simple checklist helps gardeners choose the right thickness:
- 4mm: Best for mild climates and short growing seasons.
- 6mm–8mm: Suitable for most home greenhouses.
- 10mm–16mm: Ideal for harsh climates or commercial use.
Polycarbonate panels offer flexibility for different greenhouse designs. Gardeners can select the type and thickness that fits their budget and climate.
Polycarbonate Panels vs. Other Greenhouse Materials

Polycarbonate vs. Glass
Polycarbonate offers better insulation than glass. This material traps heat inside the greenhouse, which helps plants grow in cooler climates. Glass provides a classic look and high clarity, but it does not retain heat as well.
Polycarbonate resists impacts from hail and debris. Glass can shatter easily, which may cause safety concerns. Many gardeners choose polycarbonate for its durability and long lifespan. Maintenance differs between these materials. Polycarbonate requires less cleaning and does not crack as often. Glass needs frequent washing to stay clear and may break during storms.
| Feature | Polycarbonate | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | High | Low |
| Impact Safety | Excellent | Poor |
| Maintenance | Low | High |
| Appearance | Modern | Classic |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Polycarbonate vs. PVC
Polycarbonate provides stronger insulation than PVC. This feature helps maintain stable temperatures inside the greenhouse. PVC allows less light and may not last as long. Durability sets polycarbonate apart. PVC can crack or warp under harsh weather. Polycarbonate withstands wind, rain, and sun for many years.
Cost is another factor. PVC costs less upfront, but it may need frequent replacement. Polycarbonate costs more but offers better value over time.
| Feature | Polycarbonate | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | High | Low |
| Durability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Light Diffusion | Good | Fair |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Sustainability | High | Low |
Best Greenhouse Material Comparison
Gardeners compare insulation, durability, cost, and maintenance when choosing greenhouse materials. Polycarbonate excels in insulation and impact resistance. Glass offers high clarity but lacks strong insulation. PVC provides a budget-friendly option but may not last as long.
A simple list helps gardeners decide:
- Polycarbonate: Best for insulation, safety, and long-term use.
- Glass: Best for appearance and clarity.
- PVC: Best for low cost and temporary structures.
Polycarbonate panels provide a balance of strength, insulation, and light diffusion. Gardeners who value durability and energy efficiency often select polycarbonate. Each material has strengths and weaknesses, so gardeners should match their choice to climate and gardening goals.
Choosing the Right Polycarbonate Greenhouse
Climate Considerations
Climate plays a major role in selecting a polycarbonate greenhouse. Gardeners in cold regions need thicker panels for better insulation. Multiwall polycarbonate greenhouse coverings trap heat and protect plants from frost.
In hot climates, growers benefit from polycarbonate greenhouse panels that diffuse sunlight. This feature prevents overheating and supports healthy growth. Windy areas require sturdy polycarbonate greenhouse structures to withstand strong gusts.
Humidity also affects the choice of polycarbonate greenhouse. High humidity can cause condensation inside greenhouses. Proper ventilation and panel selection help reduce moisture buildup.
Budget and Gardening Goals
Budget influences the type of polycarbonate greenhouse a gardener can build. Single-wall polycarbonate greenhouse panels cost less but offer limited insulation. Multiwall polycarbonate greenhouse options provide better energy savings over time.
Gardeners with small budgets often start with basic polycarbonate greenhouse kits. These kits use thinner polycarbonate panels and simple frames. Larger polycarbonate greenhouse projects require more investment but support year-round growth.
Gardening goals shape the choice of polycarbonate greenhouse. Hobbyists may prefer compact polycarbonate greenhouse models for seasonal use. Commercial growers select durable polycarbonate greenhouse coverings for maximum yield.
| Gardening Goal | Recommended Polycarbonate Greenhouse Type |
|---|---|
| Seasonal Growing | Single-wall polycarbonate greenhouse |
| Year-round Growing | Multiwall polycarbonate greenhouse |
| Commercial Farming | Thick multiwall polycarbonate greenhouse |
Conclusion
Polycarbonate panels give gardeners strong insulation, high light transmission, and reliable protection for greenhouses. Twin and triple wall designs help keep plants healthy by diffusing light and retaining heat. Gardeners in harsh climates or those seeking the best greenhouse material for year-round growing often choose polycarbonate panels, while beginners may prefer single wall options for seasonal use.
Twin and triple wall greenhouses support plants with balanced light and temperature. The best greenhouse material depends on climate, budget, and gardening goals. Twin and triple wall panels offer long-term value for plants.