Skylights have become a popular feature in both residential and commercial buildings, bringing natural light, aesthetic appeal, and energy efficiency to interior spaces. Choosing the right skylight material is essential, as it can influence durability, safety, and overall performance.
Builders and designers often face a key decision between glass and polycarbonate options, each offering distinct characteristics that suit different applications. Understanding how these materials compare in terms of strength, clarity, thermal insulation, and flexibility can help guide smarter choices for a variety of projects.

Overview of Skylight Materials
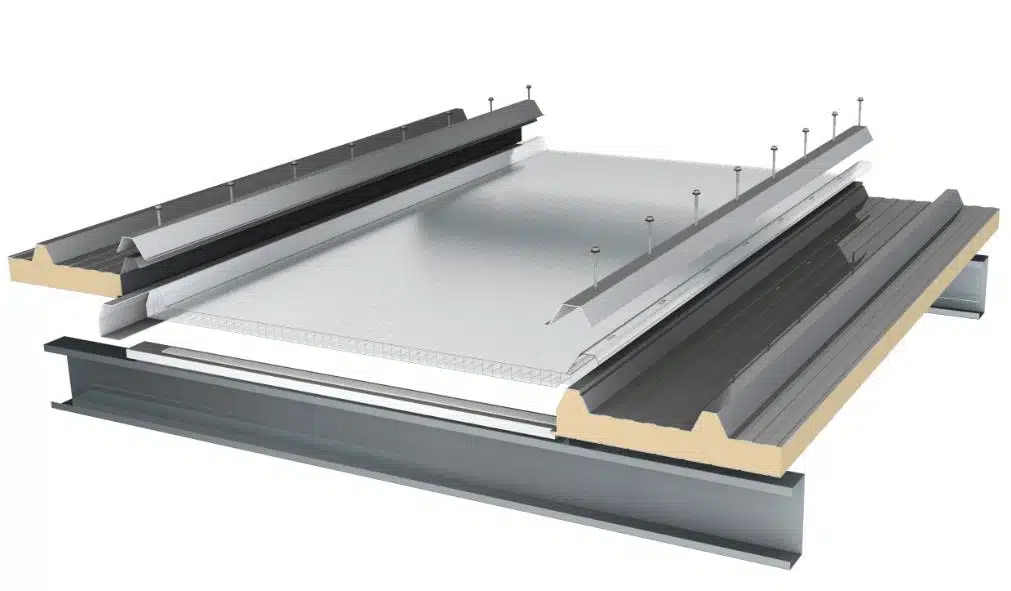
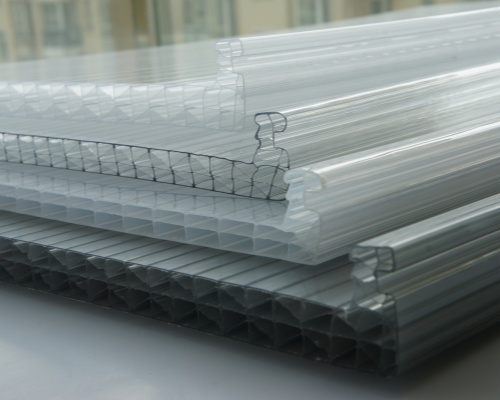
Polycarbonate Skylights
Polycarbonate skylights use a tough plastic material called polycarbonate. Polycarbonate roofing stands out for its strength and flexibility. Many builders choose polycarbonate skylights for areas that need high impact resistance.
Polycarbonate roofing can handle heavy hail and falling debris. Polycarbonate skylights weigh less than glass skylights, making installation easier. Polycarbonate also offers good thermal insulation, which helps keep buildings energy efficient.
Polycarbonate roofing costs less than glass roofing. Polycarbonate skylights resist yellowing and cracking over time. Polycarbonate remains a popular choice for projects that need durability and safety.
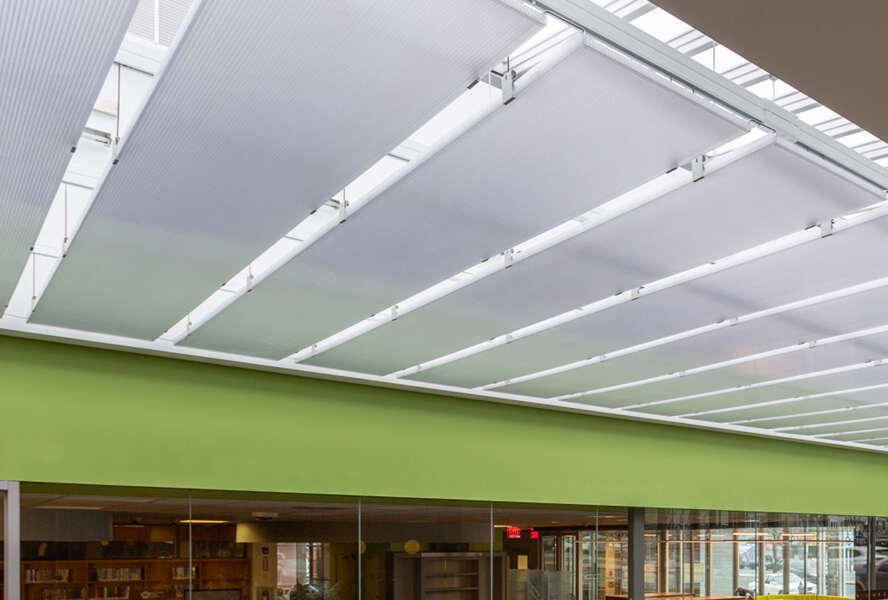
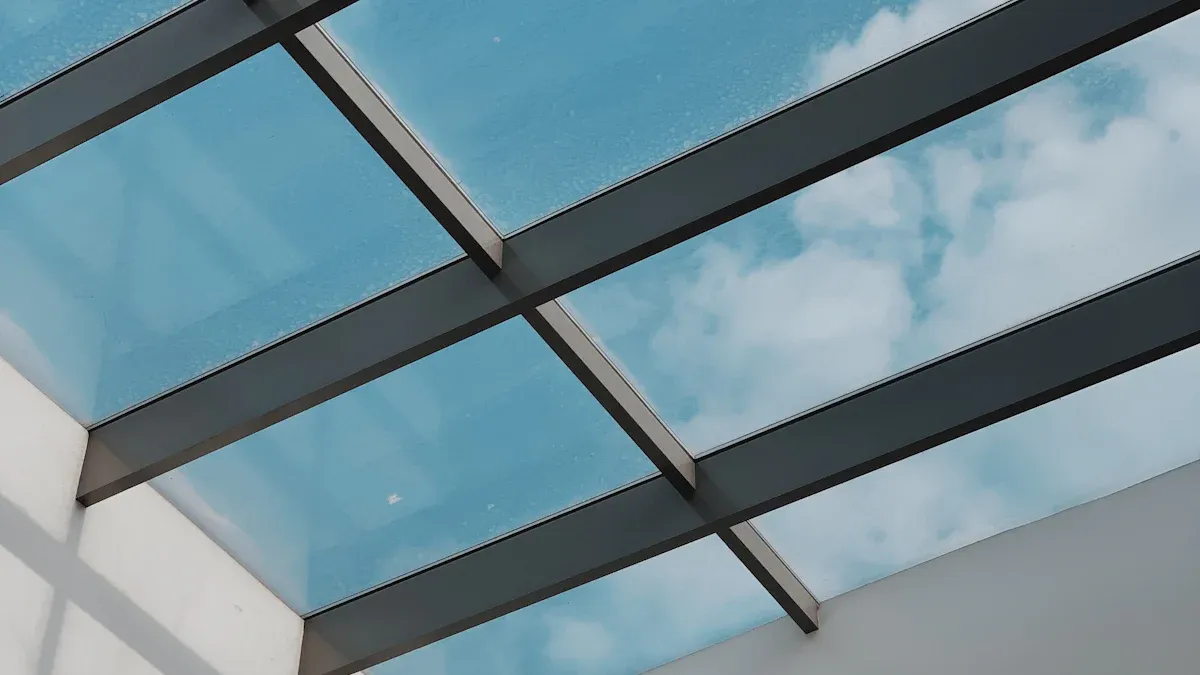
Glass Skylights
Glass skylights use glass roofing panels to let in natural light. Glass roofing gives a clear, bright view of the sky. Many people prefer glass skylights for their elegant appearance.
Glass roofing feels solid and lasts for many years. Glass skylights resist scratches better than polycarbonate skylights. Glass also keeps its clarity, so glass skylights look new for a long time.
Glass skylights need strong support because glass weighs more than polycarbonate. Glass roofing can break if hit hard, but it usually stays safe with special treatments. Glass skylights remain the top pick for high-end projects that want a premium look.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Skylight

Durability & Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate offers extreme impact resistance. It is about 250 times stronger than glass. Builders often choose polycarbonate for areas with heavy hail or flying debris because it provides excellent weather resistance.
Glass has good durability and resists scratches well. However, glass can break under strong impact. Polycarbonate remains the safer choice for locations that need extra protection.
Light Transmission & Clarity
Both polycarbonate and glass allow light to enter a space. Polycarbonate provides high transmission of light, but glass delivers the best natural daylight transmission and high clarity.
Glass skylights create a bright and clear view of the sky. Polycarbonate skylights can sometimes look less clear, but they still offer good transmission for most uses.
People who want maximum clarity often select glass, while polycarbonate works well for general lighting needs.
Thermal Insulation & Energy Efficiency
Polycarbonate skylights offer strong thermal insulation. This helps buildings stay comfortable and improves energy efficiency.
Glass skylights can also provide thermal insulation, especially when double-glazed. Polycarbonate often performs better in reducing heat loss and saving energy.
Many schools and industrial buildings use polycarbonate to lower energy costs.
Weight & Structural Requirements
Polycarbonate weighs much less than glass. Builders find polycarbonate easier to handle and install.
Glass requires stronger support structures because of its heavier weight. This can increase building costs and limit design options.
Polycarbonate suits curved roofs and unique shapes, while glass works best for flat or gently sloped skylights.
Longevity
Polycarbonate resists yellowing and cracking over time. It maintains its strength and transmission of light for many years.
Glass skylights last a long time and keep their clarity. Glass does not fade or lose transmission, but it may break if hit hard.
Both materials offer good longevity, but polycarbonate provides extra protection against harsh conditions.
Maintenance & Cleaning
Polycarbonate skylights need regular cleaning to prevent dirt buildup. They resist most stains and do not scratch easily.
Glass skylights stay clear with simple cleaning and resist scratches better than polycarbonate.
Both types require basic maintenance, but glass may need more care to avoid breakage.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
Polycarbonate Skylights
Polycarbonate skylights offer several advantages for builders and property developers
- The material weighs less than glass, which makes the installation process easier and faster.
- Workers can lift and position polycarbonate panels with less effort, reducing labor costs.
- The lighter weight also means buildings need less structural support, which can lower overall expenses.
Polycarbonate resists impacts from hail, debris, and accidental contact.
- This durability helps protect people and property in areas with harsh weather.
- The installation process often requires fewer safety precautions compared to glass.
However, polycarbonate has some drawbacks.
- The surface may scratch more easily than glass.
- Over time, exposure to sunlight can cause slight yellowing, although modern panels resist this effect better than older ones.
Glass Skylights
Glass skylights provide a classic look and clear views of the sky.
- The material stays bright and transparent for many years.
- Glass resists scratches and keeps its appearance with regular cleaning.
Glass weighs much more than polycarbonate.
- The installation process needs stronger support beams and careful handling.
- This extra weight can increase costs and limit design options for some buildings.
Glass can break if hit with strong force, even though tempered or laminated glass improves safety.
- Repairs or replacements may cost more than with polycarbonate.
- Glass skylights often require more planning before installation to ensure safety and stability.
Best Applications for Polycarbonate and Glass Skylights

Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate panels fit well in places that need strength and flexibility. Industrial buildings often face harsh weather and heavy impacts. Polycarbonate handles these challenges with ease. Schools and sports facilities use polycarbonate because it keeps people safe from flying debris. The material bends to fit curved roofs, making it a top choice for creative designs.
Polycarbonate offers strong thermal insulation. This feature helps lower heating and cooling costs in large spaces. Many builders select polycarbonate for its energy savings. The panels also provide excellent uv protection. This keeps people and equipment safe from harmful rays. Polycarbonate blocks most ultraviolet light, which helps prevent fading of furniture and flooring.
Glass
Glass skylights bring natural light and clear views into homes and offices. Many architects choose glass for its elegant look. Retail stores use glass to create bright, inviting spaces for customers. High-end projects often feature glass skylights to achieve a premium appearance.
Glass panels can include special coatings for uv protection. These coatings help block harmful rays while letting in sunlight. Double-glazed glass improves insulation, making it suitable for both warm and cold climates. Glass skylights last for many years and keep their clarity with simple cleaning.
| Application Type | Best Material | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Buildings | Polycarbonate | Impact resistance, energy savings |
| Schools/Sports Centers | Polycarbonate | Safety, uv protection |
| Curved Roofs | Polycarbonate | Flexibility, design options |
| Homes/Offices | Glass | Clarity, aesthetics, uv protection |
| Retail/High-End Projects | Glass | Premium look, durability |
Tips for Making the Right Choice
Budget, Structure & Aesthetic Goals
Buyers should start by setting a clear budget. Polycarbonate skylights usually cost less than glass options. Builders often choose polycarbonate for projects with tight budgets or where cost savings matter most.
Structural needs also play a big role. Polycarbonate weighs less, so it works well for roofs that cannot support heavy loads. Glass needs stronger support, which can increase construction costs.
Aesthetics matter for many projects. Glass skylights provide a classic, elegant look. Polycarbonate offers more flexibility for creative shapes but may not match the clarity of glass.
Consider Climate & Usage
Climate affects skylight performance. Polycarbonate handles hail, storms, and extreme weather better than glass. In areas with frequent storms, polycarbonate offers extra safety.
Building usage guides material choice. Schools, gyms, and factories benefit from polycarbonate’s impact resistance. Homes and offices often use glass for its clear views and stylish appearance.
Maintenance & Lifespan
Maintenance needs differ between materials. Glass resists scratches and stays clear with regular cleaning. Polycarbonate may need more frequent cleaning but resists impacts and cracking.
Lifespan also matters. Both materials last for many years, but polycarbonate stands up better to harsh conditions. Glass keeps its clarity longer if protected from strong impacts.
| Factor | Polycarbonate | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Weight | Light | Heavy |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Clarity | Good | Excellent |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Low |
The glass vs polycarbonate debate centers on clarity, strength, and cost. Glass vs polycarbonate skylights differ in impact resistance, with polycarbonate offering more protection. Many choose glass vs polycarbonate for its elegant look, while others value the energy efficiency of polycarbonate. When comparing glass vs polycarbonate, buyers should match their needs to the right material for their project.
Conclusion
Choosing the right skylight depends on project needs. Polycarbonate skylights offer impact resistance, lightweight installation, flexibility, and energy efficiency, ideal for industrial buildings, schools, and sports facilities. Glass skylights provide superior clarity, elegant aesthetics, and long-term durability, perfect for homes, offices, and high-end projects. By considering budget, structure, appearance, climate, and maintenance, builders can confidently select the skylight that balances performance, safety, and style.